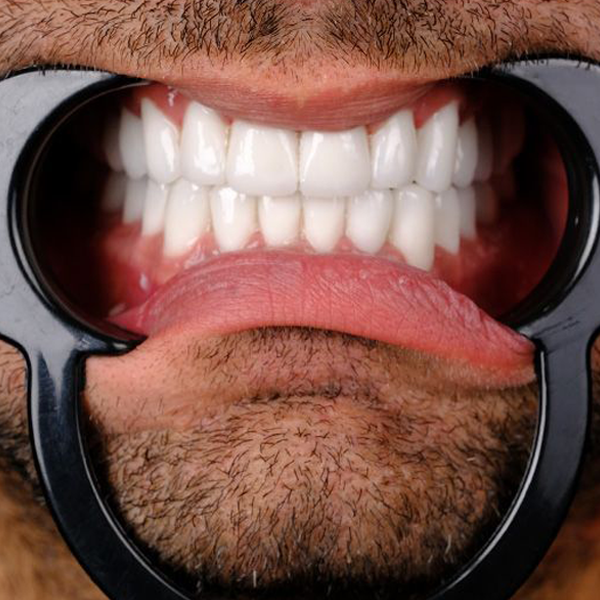
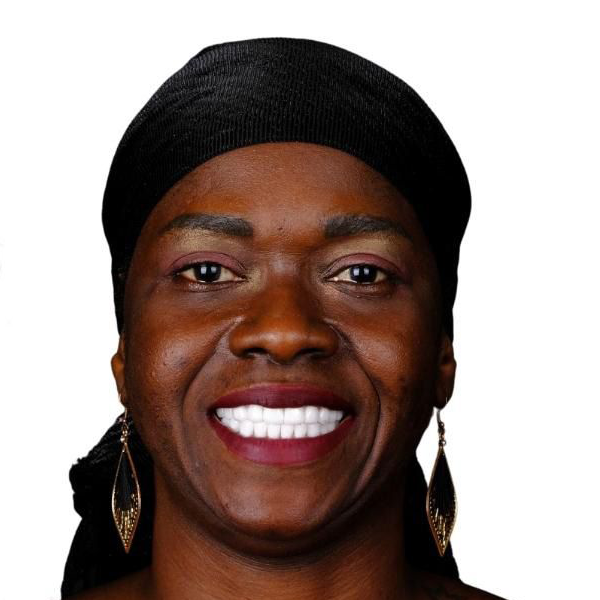
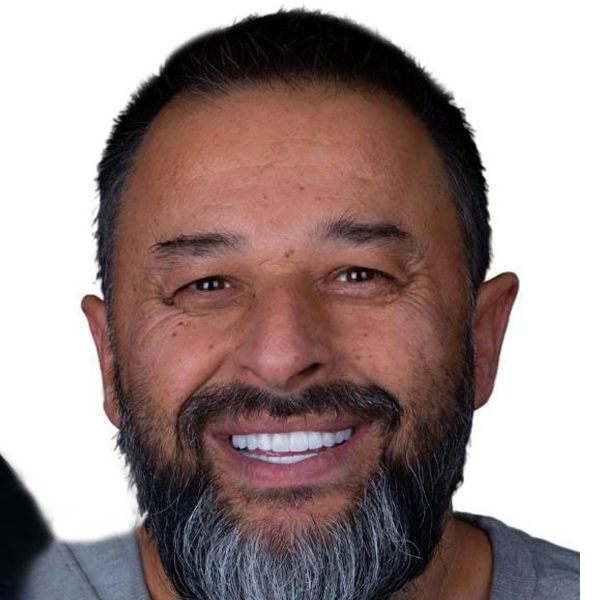
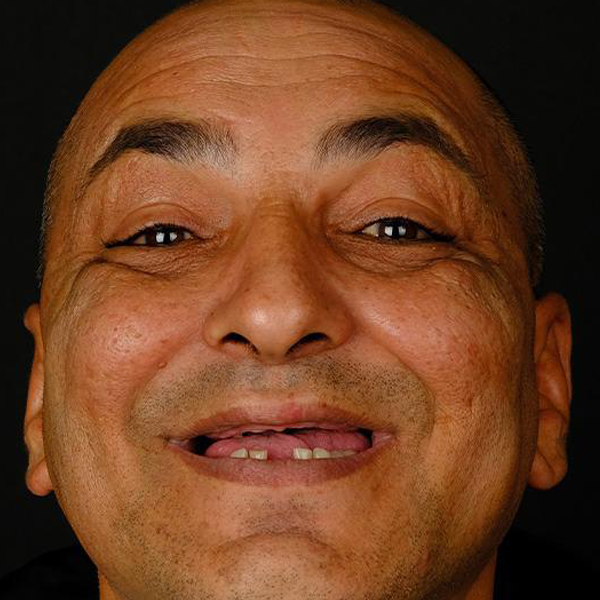
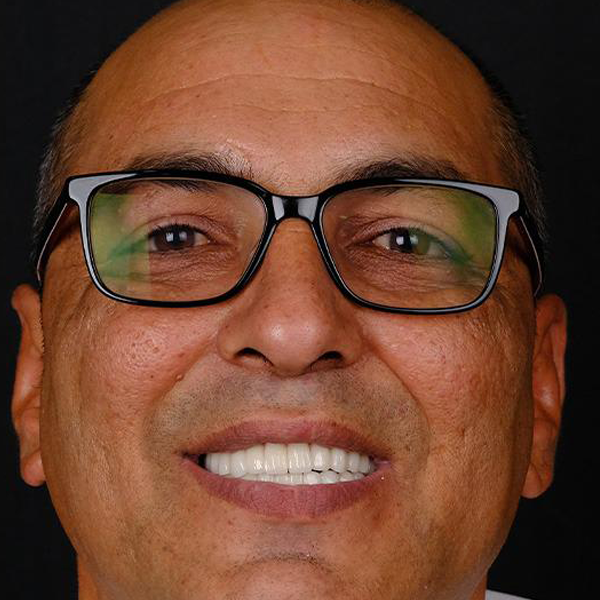
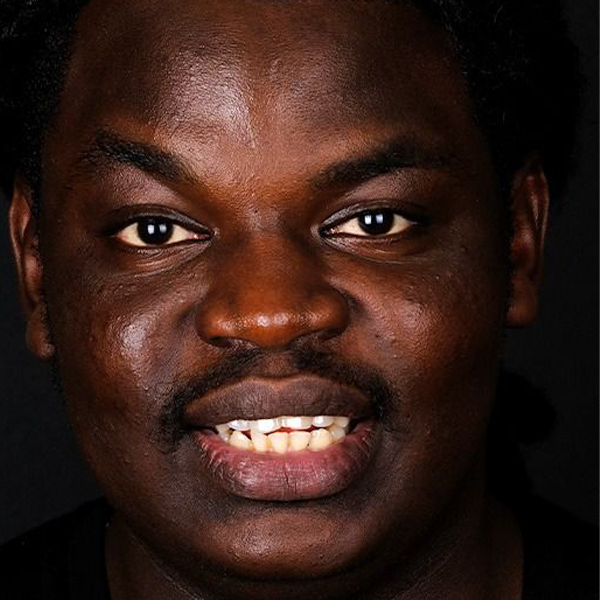
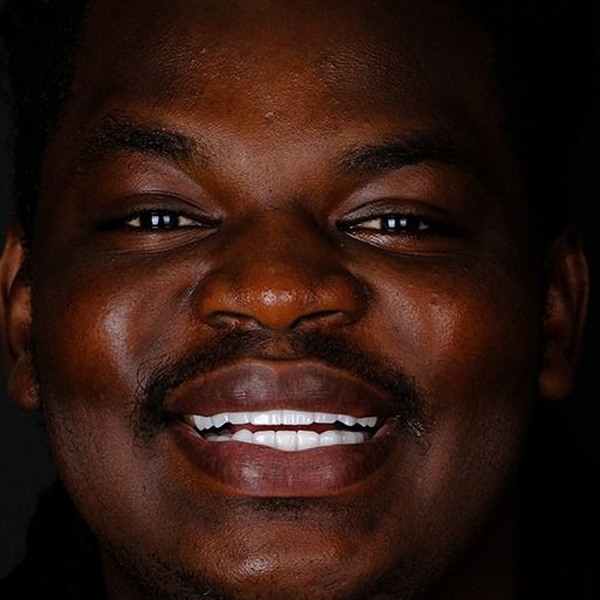
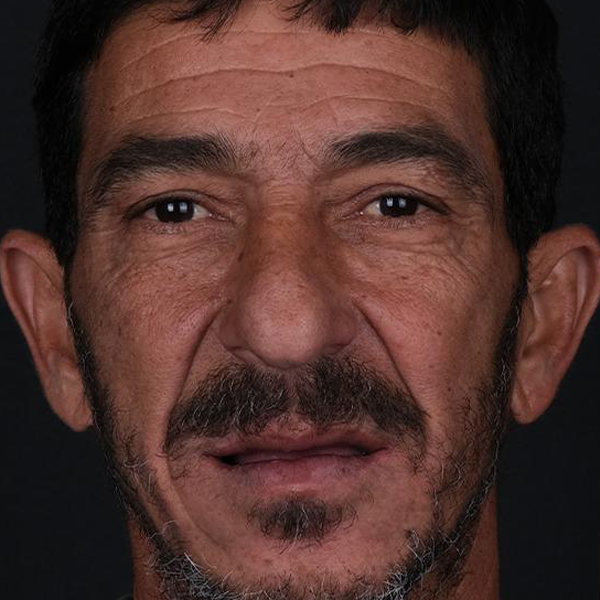
Dentistry
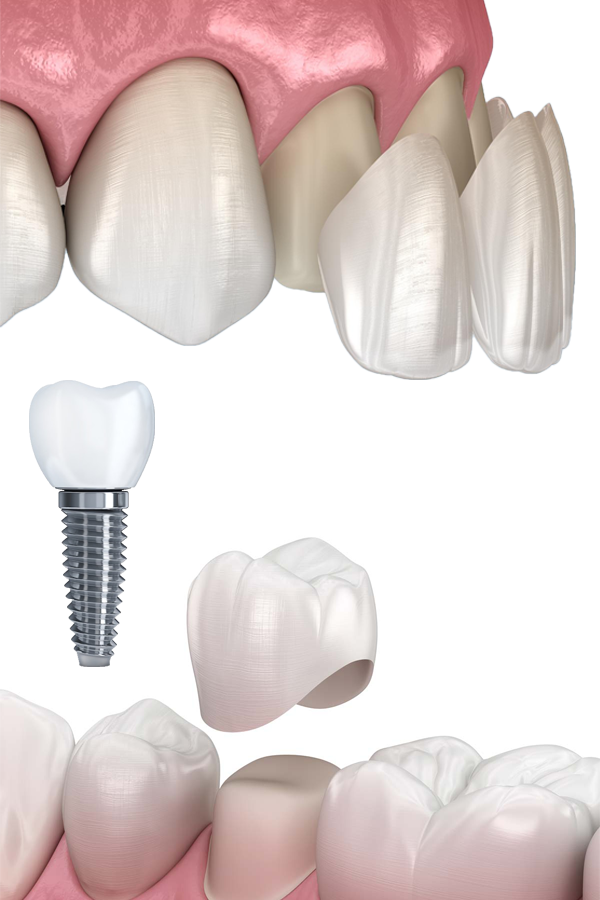
Dental treatments encompass a wide range of procedures aimed at maintaining oral health, addressing dental issues, and enhancing the appearance of the teeth and gums. Here are some common dental treatments:
- Dental Crowns: Crowns are placed over damaged or weakened teeth to restore their shape, strength, and appearance. They can be made from various materials, including porcelain, metal, or a combination.
- Dental Bridges: Bridges are used to replace missing teeth by anchoring artificial teeth (pontics) to adjacent natural teeth or dental implants.
- Dental Implants: Implants are used to replace missing teeth. A titanium post is surgically placed in the jawbone, and a crown is attached to the post, creating a natural-looking tooth replacement.
- Teeth Whitening: Professional teeth whitening procedures can remove stains and discoloration, brightening the teeth’s appearance.
- Orthodontic Treatment: Orthodontic treatments, such as braces or clear aligners, are used to correct misaligned teeth and improve the bite.
- Dentures: Dentures are removable appliances used to replace missing teeth and surrounding tissues. They can be partial or full, depending on the patient’s needs.
- Dental Veneers: Veneers are thin shells made of porcelain or composite resin that are bonded to the front surfaces of teeth to improve their appearance.
These are just a few examples of common dental treatments. The specific treatments recommended for an individual depend on their oral health needs and concerns. It’s important to maintain regular dental checkups to receive professional advice and treatment tailored to your unique situation.
















































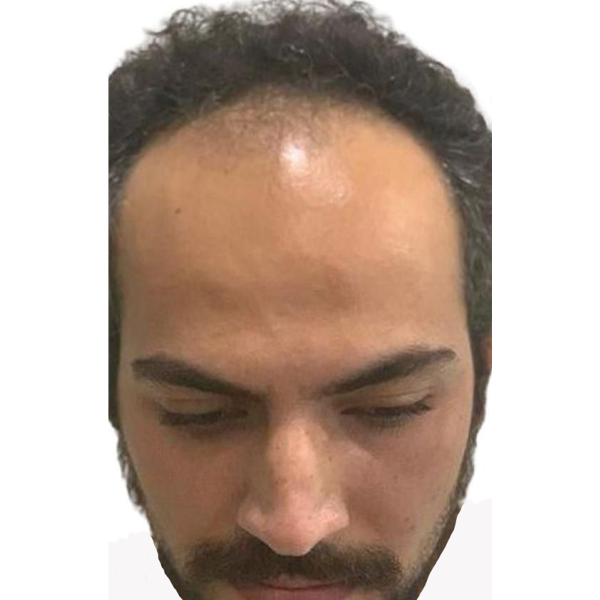
Hair Transplant

Hair transplant is a surgical procedure designed to treat hair loss and restore hair growth in areas where hair has become thin or bald. The most common method used for hair transplant is known as follicular unit transplantation (FUT) or follicular unit extraction (FUE). Here's an overview of the hair transplant process: 1. Consultation: Before the procedure, you'll have a consultation with a hair transplant specialist. During this consultation, your doctor will assess your hair loss pattern, discuss your expectations, and determine if you're a suitable candidate for the procedure. 2. Preparation: On the day of the procedure, the surgical team will prepare the area where the hair follicles will be harvested (usually the back or sides of the head). The area will be cleaned, and the hair will be trimmed short. 3. Anesthesia: Local anesthesia will be administered to numb both the donor area (where hair follicles are harvested) and the recipient area (where the hair will be transplanted). This ensures that the procedure is comfortable and pain-free. 4. Harvesting Hair Follicles: There are two main methods for harvesting hair follicles: FUT and FUE. FUT (Strip Method): In FUT, a strip of skin containing hair follicles is removed from the donor area. The wound is then sutured closed. The strip is dissected into individual follicular units under a microscope. FUE (Follicular Unit Extraction): In FUE, individual hair follicles are extracted directly from the donor area using a specialized instrument. This method doesn't require a strip of skin to be removed. 5. Graft Preparation: The harvested follicles are carefully prepared for transplantation. This involves separating them into individual follicular units containing one to four hairs each. 6. Recipient Site Creation: Tiny incisions are made in the recipient area according to the natural hair growth pattern. The angle, direction, and density of the incisions are critical to achieving a natural look. 7. Implantation: The prepared follicular units are meticulously placed into the recipient sites. This step requires precision and attention to detail to ensure the transplanted hairs align with the natural hair growth. 8. Post-Procedure Care: After the procedure, you'll be provided with instructions on how to care for the transplanted area. This includes information on cleaning, avoiding certain activities, and taking any prescribed medications. 9. Recovery and Results: The transplanted hair will initially shed within a few weeks. However, the hair follicles remain intact beneath the skin. New hair growth will begin within a few months, gradually becoming thicker and more natural-looking over time. 10. Follow-Up: You'll likely have follow-up appointments with your doctor to monitor your progress and address any concerns. Multiple sessions may be required to achieve the desired density and coverage. It's important to note that the success of a hair transplant depends on various factors, including the surgeon's skill, the patient's hair characteristics, and post-procedure care. Consulting with a qualified and experienced hair transplant specialist is essential to determine the most suitable approach and expected outcomes for your specific situation.
DHI Transplant
DHI (Direct Hair Implementation) is a hair transplant method that uses a pen device. It can help both men and women restore hair loss and increase hair density because it is one of the most recent techniques in the hair restoration industry.
Sapphire FUE Hair Transplant
Follicular Unit Extraction, Sapphire FUE, is a type of hair transplant that has become the most preferred method for many reasons. It is a minimally invasive operation.
Beard Transplant
For men who lack facial hair, beard transplantation is a cosmetic procedure for implanting hair follicles on the beard area.
Women Hair Transplant
We understand that female-pattern baldness is different from male’s. That’s why we find precise solutions for hair loss for our female patients.









IVF
In vitro fertilization (IVF) is a complex assisted reproductive technology used to help individuals or couples conceive a child when other methods have not been successful. IVF involves fertilizing an egg with sperm outside the body and then transferring the resulting embryo(s) into the uterus. Here’s an overview of the IVF treatment process:
1. Ovulation Induction: The process begins with the woman taking hormonal medications (usually injections) to stimulate the ovaries to produce multiple eggs instead of the usual one egg per cycle. Monitoring through ultrasound and blood tests helps track the growth of follicles (fluid-filled sacs containing eggs). 2. Egg Retrieval (Oocyte Retrieval): Once the follicles have matured, a minor surgical procedure is performed to retrieve the eggs. This is typically done under sedation or anesthesia. A thin needle is guided through the vaginal wall to the ovaries to collect the eggs. 3. Sperm Collection: A sperm sample is collected from the male partner or a sperm donor. The sperm is then prepared in the laboratory to select the healthiest and most motile sperm for fertilization. 4. Fertilization: There are different methods of fertilization used in IVF: Conventional IVF: The retrieved eggs are mixed with the prepared sperm in a laboratory dish for fertilization to occur naturally. Intracytoplasmic Sperm Injection (ICSI): A single sperm is directly injected into each mature egg to facilitate fertilization, especially in cases of male infertility. 5. Embryo Culture: After fertilization, the embryos are cultured in a controlled environment for a few days as they develop and divide. 6. Embryo Selection: The embryologist examines the embryos' development and selects the healthiest and most viable ones for transfer. The number of embryos transferred depends on various factors, including the patient's age and medical history. 7. Embryo Transfer: A selected number of embryos are transferred into the woman's uterus. This is a relatively simple procedure that doesn't usually require anesthesia. The embryos are placed into the uterus using a thin catheter inserted through the cervix. 8. Luteal Phase Support: After the embryo transfer, the woman may be given progesterone or other medications to support the uterine lining and increase the chances of implantation. 9. Pregnancy Test: About 10-14 days after the embryo transfer, a blood test is conducted to determine if the woman is pregnant. If the test is positive, further monitoring and ultrasound scans will follow to track the pregnancy's progress. 10. Cryopreservation (Freezing): Any viable embryos not transferred during the initial cycle can be frozen for future use (cryopreserved) in case additional cycles are needed. IVF can be emotionally and physically challenging, and success rates vary depending on factors such as the woman's age, underlying fertility issues, and the clinic's expertise. It's important to consult with a fertility specialist to discuss your individual situation, expectations, and potential outcomes before undergoing IVF treatment.
Feel your body like you never did
Bariatric surgery, also known as weight loss surgery, is a group of surgical procedures designed to help individuals with severe obesity achieve significant and sustainable weight loss. These surgeries aim to reduce the size of the stomach and/or alter the digestive process to limit the amount of food that can be consumed and absorbed. Here are some common types of bariatric surgeries: 1. Gastric Bypass (Roux-en-Y): Gastric bypass surgery involves creating a small pouch at the top of the stomach, which is then connected directly to the small intestine. This bypasses a portion of the stomach and the first part of the small intestine. The reduced stomach size and altered digestion result in both restriction and malabsorption, leading to weight loss. 2. Sleeve Gastrectomy: During a sleeve gastrectomy, a large portion of the stomach is removed, leaving a smaller banana-shaped pouch. This reduces the stomach's capacity and also affects hunger-regulating hormones, contributing to weight loss. 3. Adjustable Gastric Banding (Lap-Band): In this procedure, an inflatable band is placed around the upper part of the stomach, creating a small pouch and limiting food intake. The band's tightness can be adjusted over time to control the rate of weight loss. 4. Biliopancreatic Diversion with Duodenal Switch (BPD/DS): This is a complex surgery that combines a sleeve gastrectomy with a significant portion of the small intestine being bypassed. It results in both restriction and malabsorption, leading to substantial weight loss. 5. Intragastric Balloon: An intragastric balloon is a non-surgical option that involves placing a deflated balloon in the stomach, which is then filled with saline. The balloon takes up space in the stomach, leading to a feeling of fullness and reduced food intake. Benefits of Bariatric Surgery: Significant Weight Loss: Bariatric surgery can lead to substantial and sustained weight loss, improving overall health and quality of life. Improvement in Health Conditions: Many obesity-related health conditions, such as type 2 diabetes, high blood pressure, and sleep apnea, often improve or resolve after surgery. Enhanced Mobility: Weight loss can result in improved mobility, reduced joint pain, and increased physical activity. Psychological Well-Being: Bariatric surgery can lead to improved self-esteem and body image, as well as reduced risk of depression and anxiety. Risks and Considerations: Bariatric surgery carries risks such as infection, bleeding, blood clots, and complications related to anesthesia. Nutritional deficiencies may occur due to reduced food intake or malabsorption, requiring lifelong vitamin and mineral supplementation. Changes in diet, lifestyle, and long-term follow-up are essential for successful outcomes. Bariatric surgery is a serious decision that should be thoroughly discussed with healthcare professionals. A comprehensive evaluation of the potential benefits and risks, along with a commitment to post-surgery lifestyle changes, is crucial for long-term success.
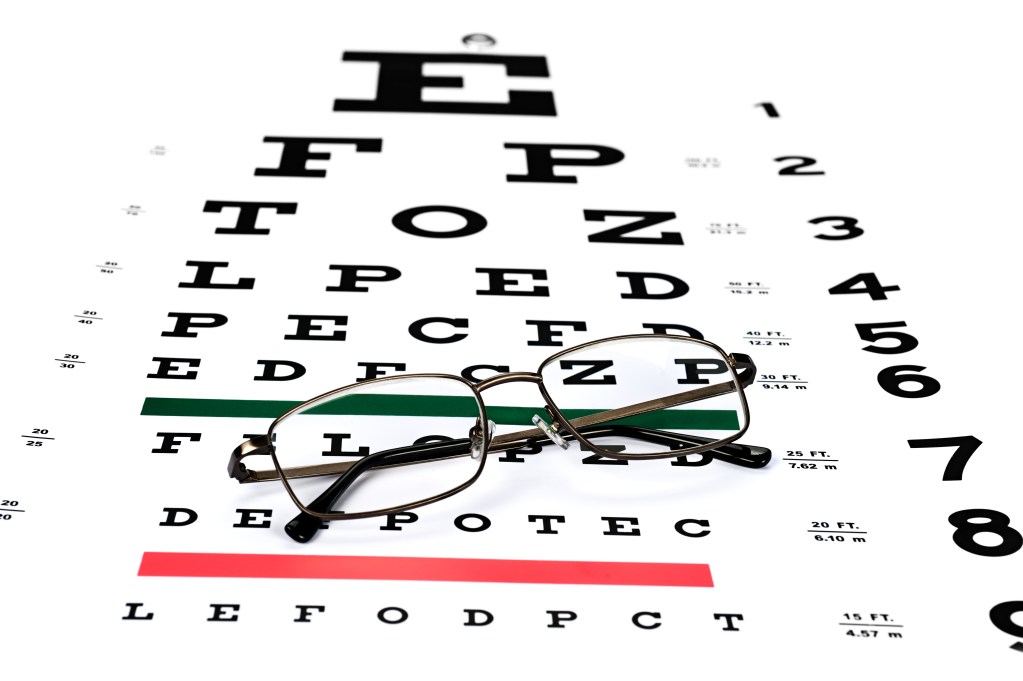
LASIK, or Laser-Assisted In Situ Keratomileusis, is a surgical procedure that uses a laser to reshape the cornea of the eye. This helps improve the way light enters the eye, correcting vision problems such as nearsightedness, farsightedness, and astigmatism. LASIK is a common and effective method to reduce or eliminate the need for glasses or contact lenses. However, candidacy depends on factors like overall eye health, and it’s important to consult with an eye care professional to determine suitability.

Aesthetic Surgeries
Aesthetic surgeries, also known as cosmetic surgeries or plastic surgeries, are medical procedures performed to enhance a person’s appearance by altering or rejuvenating specific features of the face or body. These surgeries are elective and are typically chosen by individuals who wish to improve their self-confidence and achieve their desired aesthetic goals. Here are some common types of aesthetic surgeries:
1. Rhinoplasty (Nose Job): Rhinoplasty involves reshaping and altering the size and/or shape of the nose to enhance facial harmony and proportions. 2. Facelift (Rhytidectomy): A facelift is a procedure that aims to reduce visible signs of aging by tightening sagging facial skin and muscles, resulting in a more youthful appearance. 3. Blepharoplasty (Eyelid Surgery): Blepharoplasty involves removing excess skin, fat, and muscle from the eyelids to rejuvenate the eyes and achieve a more rested and youthful look. 4. Liposuction: Liposuction is a procedure that removes excess fat deposits from various parts of the body, helping to contour and reshape areas such as the abdomen, thighs, hips, and arms. 5. Breast Augmentation: Breast augmentation involves using implants to increase the size and fullness of the breasts, enhancing the overall body proportions. 6. Breast Reduction: Breast reduction surgery removes excess breast tissue and skin to reduce the size and weight of the breasts, alleviating discomfort and improving body balance. 7. Tummy Tuck (Abdominoplasty): A tummy tuck involves removing excess skin and fat from the abdomen, tightening the abdominal muscles, and creating a flatter and firmer abdominal contour. 8. Lip Augmentation: Lip augmentation enhances lip volume and shape using injectable fillers or implants to create a fuller and more youthful appearance. 9. Botox and Dermal Fillers: Botox injections and dermal fillers are non-surgical procedures used to reduce wrinkles, restore volume, and improve facial contours. 10. Brazilian Butt Lift: This procedure involves removing fat from one part of the body through liposuction and injecting it into the buttocks to enhance their shape and volume. 11. Mommy Makeover: A mommy makeover is a combination of procedures (such as breast augmentation, tummy tuck, and liposuction) designed to address post-pregnancy body changes. It's important to note that aesthetic surgeries, like any medical procedures, carry potential risks and considerations. Consulting with a board-certified plastic surgeon or a qualified aesthetic practitioner is crucial to discuss your goals, assess your suitability for surgery, and understand the potential outcomes, risks, and recovery process. The decision to undergo an aesthetic surgery should be well-informed and made in consultation with a medical professional.
Why you will love our tours
“Experience Exceptional Care: Our medical tours offer top-tier healthcare combined with personalized attention, ensuring your well-being is our priority.
Expert Specialists: Access renowned medical experts and specialists who are dedicated to providing you with the best possible care.
Cutting-Edge Facilities: Benefit from state-of-the-art medical facilities equipped with the latest technologies and advancements.

Contact
Merkez Mahallesi 675.Sokak Bağcılar /İSTANBUL /Turkey
+90 (541) 313 8600
A WordPress.com website







